施工実績

Understanding Period Costs in Accounting and Management
2022.05.27
What a company expects to pay during a particular accounting period is included in an expense account while what it pays during the period goes into a prepaid expense account. Period expenses https://www.bookstime.com/ are costs that help a business or other entity generate revenue, but aren’t part of the cost of goods sold. Resources consumed to provide or maintain the organization’s capacity to produce or sell are capacity costs or supportive overheads. Standby costs will continue if the firm shuts down operations or facilities temporarily.
What is a period expense?
- A good example of this would be the interest incurred on a loan for office equipment that isn’t directly tied to the production of products, as long as that interest is paid within the accounting period.
- Period expenses are usually calculated by adding together all expected payments for a period, then subtracting any amounts that were paid early.
- Understanding the difference between these two types of costs is crucial for making informed investment decisions, optimizing operations, improving profitability, and accurately reporting financial performance.
- FIFO costing does not mix costs from prior tenure (in beginning inventory) with a current period expense.
Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. Managers are always on the lookout for ways to reduce costs while trying to improve the overall effectiveness of their operations. Examples include production materials consumed in making a product and commissions paid to salespeople. Focusing on these areas of your business can shorten the time it takes to recoup acquisition expenses and drive meaningful improvements across your business metrics. Product costs (also known as inventoriable costs) are costs assigned to products.
To Ensure One Vote Per Person, Please Include the Following Info
Moreover, it helps authorities identify the irrelevant unavoidable costs that will always consider reaching the breakeven point. While the concept sounds straightforward—measuring how long it takes to recoup the cost of acquiring a customer—the reality involves nuanced calculations and interpretations. Some companies use a simple formula for quick insights, while others prefer a more detailed approach that accounts for profit margins and other factors. It reveals how quickly a company can recover its investments in acquiring new customers—essential information for founders, executives, and investors to track how to calculate period costs the long-term ability of the business to scale. Product Costs are essential for calculating the cost of goods sold and determining the gross profit margin of a business.
- However, not all Period Costs can be directly allocated, especially those that benefit multiple cost objects simultaneously.
- Operating expenses are costs that businesses expect to incur in their attempts to generate revenue.
- The direct materials, direct labor and manufacturing overhead costs incurred to manufacture these 500 units would be initially recorded as inventory (i.e., an asset).
- These expenses are charged to the statement of profit & loss and are not directly related to production.
- ABC provides a more accurate understanding of cost behavior and cost drivers, enabling businesses to make more informed decisions about pricing, product mix, and process improvement.
- In some cases, it will be too expensive for a company to eliminate certain types of period costs from its operations.
What are the Examples of Period Costs?

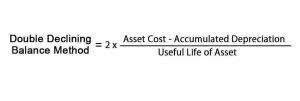
Additionally, businesses must periodically assess the carrying value of assets for impairment and adjust depreciation estimates as needed to reflect changes in asset values or useful lives. Recognizing the importance of Period Costs in financial analysis allows businesses to make informed bookkeeping decisions, optimize performance, and achieve long-term success and sustainability. They are also included in determining the amount of revenue that has been earned when an asset is sold, which in turn can affect both revenues and costs in future accounting periods.
- The management accountant must carefully evaluate the time expenditure to see if it will be included in the income statement.
- Product costs are typically recorded as assets on a company’s balance sheet and are expensed out over the life of the product.
- Companies may decide to absorb certain period costs temporarily to gain market share or enter a new market, setting prices that are competitive yet may not fully cover these expenses in the short term.
- Period costs are also listed as an expense in the accounting period in which they occur.
- There is no fixed approach to identifying the period expense in all the particulars.
Accounting for Period Costs
Smaller startups often face extended payback periods due to higher upfront costs and limited revenue streams. Conversely, mature companies might achieve shorter periods as they benefit from established customer bases and economies of scale. Industry norms also play a role; enterprise-focused SaaS companies typically see longer payback periods than consumer-facing SaaS businesses, given their larger deal sizes and sales cycles. By following these steps and formulas, businesses can accurately calculate their period cost, providing valuable insights into their financial performance and profitability. Operating expenses are expenses related to daily operations, whereas period expenses are those costs that have been paid during the current accounting period but will benefit future periods.

Product costs are typically recorded as assets on a company’s balance sheet and are expensed out over the life of the product. An example of a product cost would be the cost of raw materials used in the manufacturing process. Product costs also include Depreciation on plant, expired insurance on plant, production supervisor salaries, manufacturing supplies used, and plant maintenance. The preceding list of period costs should make it clear that most of the administrative costs of a business can be considered period costs. Examples of period expenses include vendor bills, storage for supplies or inventory not generating revenue, borrowing money to cover current costs, etc.




